
In general, the book value of equity depends on the industry that a company operates in, and how it manages its assets. Measuring the Value of a ClaimA good measure of the value of a stockholder’s residual claim at any given point in time is the book value of equity per share (BVPS). Book value is the accounting value of the company’s assets less all claims senior to common equity (such as the company’s liabilities). In the food chain of corporate security investors, equity investors do not have the first crack at operating profits. Common shareholders get whatever is left over after the corporation pays its creditors, preferred shareholders and the tax man.
What Does a Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio of 1.0 Mean?
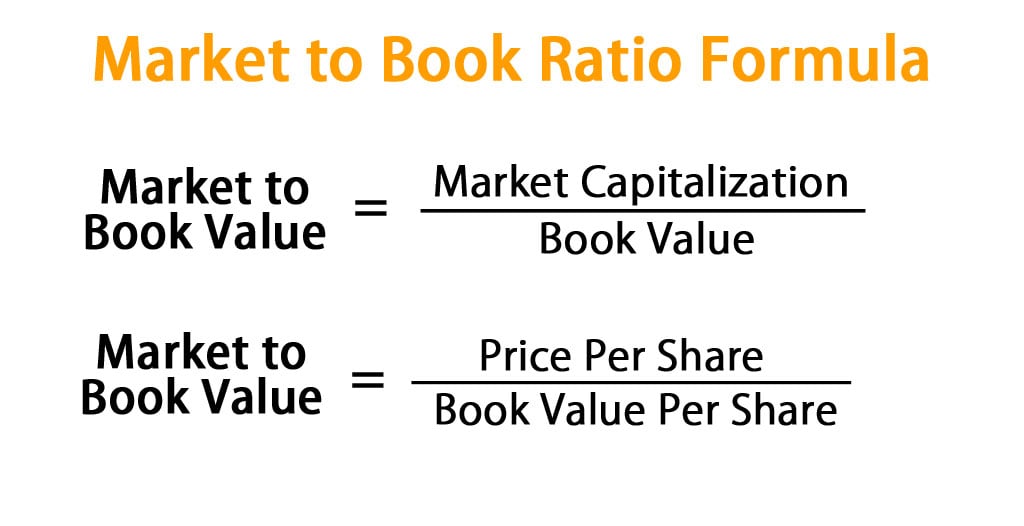
For the purpose of disclosure, companies break these three elements into more refined figures for investors to examine. Investors can calculate valuation ratios from these to make it easier to compare companies. Among these, the book value and the price-to-book ratio (P/B ratio) are staples for value investors.
- On to the next line item, “Retained Earnings” refers to the portion of net income (i.e. the bottom line) that is retained by the company, rather than issued in the form of dividends.
- However, it may also indicate overvalued or overbought stocks trading at high prices.
- Still, there are a few tactics that can help you discover value-rich investments for your portfolio.
- As noted, book value and the metrics derived from it come from balance sheet numbers — which may not be a true representation of value.
- Note that if the company has a minority interest component, the correct value is lower.
- In fact, this means that the market is not that confident in the company’s ability to generate profits in the future, but, on the other hand, value investors believe that the market is not correct.
Examples of Book Value of Equity Calculations (with Excel Template)
For example, Walmart’s January 31, 2012 balance sheet indicates that shareholders’ equity has a value of $71.3 billion. The number is clearly stated as a subtotal in the equity section of the balance sheet. To calculate BVPS, you need to find the number of shares outstanding, which is also usually stated parenthetically next to the common stock label (on Yahoo! Finance, it’s located in Key Statistics). What we’re looking for is the number of shares outstanding, not simply issued. The two numbers can be different, usually because the issuer has been buying back its own stock.
The Formula for Book Value Per Common Share Is:
Book value per share (BVPS) tells investors the book value of a firm on a per-share basis. Investors use BVPS to gauge whether a stock price is undervalued by comparing it to the firm’s market value per share. Book value refers to a firm’s net asset value (NAV) or its total assets minus its total liabilities. The market value is the value of a company according to the financial markets. The market value of a company is calculated by multiplying the current stock price by the number of outstanding shares that are trading in the market. The good news is that the number is clearly stated and usually does not need to be adjusted for analytical purposes.
Creditors who provide the necessary capital to the business are more interested in the company’s asset value. Therefore, creditors use book value to determine how much capital to lend to the company since assets make good collateral. The book valuation can also help to determine a company’s ability to pay back a loan over a given time. Some of these adjustments, such as depreciation, may not be easy to understand and assess. If the company has been depreciating its assets, investors might need several years of financial statements to understand its impact.
In theory, the book value of equity should represent the amount of value remaining for common shareholders if all of the company’s assets were to be sold to pay off existing debt obligations. The Book Value of Equity (BVE) is the residual proceeds received by the common shareholders of a company if all of its balance sheet assets were to be hypothetically liquidated. Book value per share is a way to measure the net asset value that investors get when they buy a share of stock. Investors can calculate book value per share by dividing the company’s book value by its number of shares outstanding.
Typically, the market value almost always exceeds the statement balance vs current balance, barring unusual circumstances.
A company’s stock buybacks decrease the book value and total common share count. Stock repurchases occur at current stock prices, which can result in a significant reduction in a company’s book value per common share. Both book and market values offer meaningful insights into a company’s valuation.
